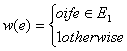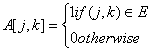CSE GATE sample paper
Printed From: One Stop GATE
Category: GATE Previous Years Test Papers - Discuss Here
Forum Name: CS Papers
Forum Discription: Computer Science Previous Year GATE Papers to can discussed here.
URL: http://forum.onestopgate.com/forum_posts.asp?TID=83
Printed Date: 28Aug2025 at 12:11am
Topic: CSE GATE sample paper
Posted By: Arpita
Subject: CSE GATE sample paper
Date Posted: 05Jan2007 at 5:58pm
|
1. If all permutations are equally likely, what is the expected number of inversions in a randomly chosen permutation of 1...n ? (a) n(n -1)/2 (b) n(n -1)/4 (c) n(n + 1)/4 (d) 2n[log2n]
2. What would be the worst case time complexity of the Insertion Sort algorithm, if the inputs are restricted to permutations of 1...n with at most n inversions? (a) Q (n 2) (b) Q (n log n) (c) Q (n 1.5) (d) Q (n)
3. A data structure is required for storing a set of integers such that each of the following operations can be done in (log n) time, where n is the number of elements in the set.
Which of the following data structures can be used for this purpose? (a) A heap can be used but not a balanced binary search tree (b) A balanced binary search tree can be used but not a heap (c) Both balanced binary search tree and heap can be used (d) Neither balanced binary search tree nor heap can be used
4. Let S be a stack of size n ³ 1. Starting with the empty stack, suppose we push the first n natural numbers in sequence, and then perform n pop operations. Assume that Push and Pop operation take X seconds each, and Y seconds elapse between the end of one such stack operation and the Blurt of the next operation. For m ³ 1, define the stack-life of m as the time elapsed from the end of Push(m) to the start of the pop operation that removes m from S. The average stack-life of an element of this stack is
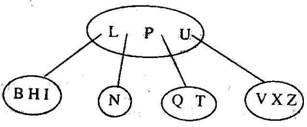
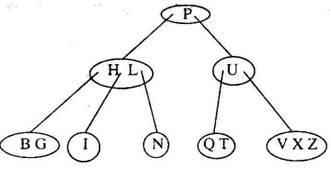
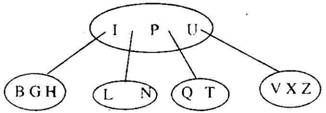
5. Consider the following 2-3-4 tree (i.e., B-tree with a minimum degree of two) in which each data item is a letter. The usual alphabetical ordering of letters is used in constructing the tree
What is the result of inserting G in the above tree ? (a)
(b)
(c)
(d) None of the above
6. The cube root of a natural number n is defined as the largest natural number m such that m 3 £ n. The complexity of computing the cube root of n (n is represented in binary notation) is
7. Let G = (V, E) be an undirected graph with a sub graph G 1 = (V 1, E 1). Weights are assigned to edges of G as follows:
A single-source shortest path algorithm is executed on the weighted graph (V, E, w) with an arbitrary vertex v 1 of V 1 as the source. Which of the following can always be inferred from the path costs computed?
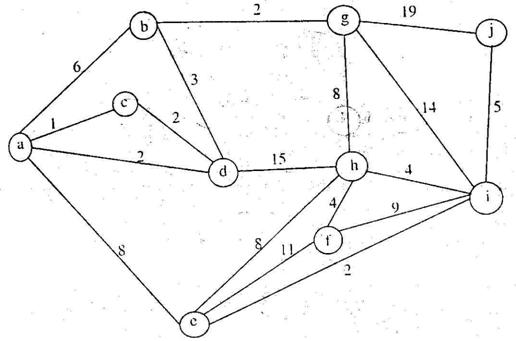
8. What is the weight of a minimum spanning tree of the following graph?
9. The following are the starting and ending times of activities A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H respectively in chronological order: "a s b s a s a e d s a e e s f s b e d e g s e e f e h s g e h e". Here, x s denotes the starting time and X e denotes the ending time of activity X. W need to schedule the activities in a set of rooms available to us. An activity can be scheduled in a room only if the room is reserved for the activity for its entire duration. What is the minimum number of rooms required?
(a) 3 (b) 4 (c) 5 (d) 6
10. Let G = (V, E) be a directed graph with n vertices. A path from V i to V j in G is sequence of vertices (V i, v i+1, ..., V j) such that (V k, V k+1) Î E for all k in i through j -1. A simple path is a path in which no vertex appears more than once. Let A be an n x n array initialized as follow
Consider the following algorithm. for i = 1 to n for j = 1 to n for k = 1 to n A [j, k] = max (A[j, k] (A[j,i] + A [i, k]);
Which of the following statements is necessarily true for all j and k after terminal of the above algorithm?
11. Consider the following logic program P A (x) ¬ B (x, y), C (y) ¬ B (x, x) Which of the following first order sentences is equivalent to P ? (a) ( " x) [( $ y) [B (x, y) Ù C (y)] Þ A (x) ] Ù Ø ( $ x) [B(xx)] (b) ( " x) [( " y) [B (x, y) Ù C (y)] Þ A (x) ] Ù Ø ( $ x) [B(xx)] (c) ( " x) [( $ y) [B (x, y) Ù C (y)] Þ A (x) ] Ú Ø ( $ x) [B(xx)] (d) ( " x) [( " y) [B (x, y) Ù C (y) Þ A (x) Ù ( $ x) [B(xx)]
12. The following resolution rule is used in logic programming: Derive clause (P Ú Q) from clauses (P Ú B), (Q Ú Ø R) Which of the following statements related to this rule is FALSE?
THE Q FOLLOWING INFORMATION PERTAINS TO Q. 73-741 The following program fragment is written in a programming language that allows variables and does not allow nested declarations of functions. global int i = 100, j =5; , void P (x) { int i = 10; print (x + 10); i = 200; j = 20; print (x); } main ( ) {P (i + j);} 13. If the programming language uses static scoping and call by need parameter passing mechanism, the values printed by the above program are (a) 115, 220 (b) 25, 220 (c) 25, 15 (d) 115,105
14. If the programming language uses dynamic scoping and call by name parameter passing mechanism, the values printed by the above program are (a) 115,220 (b) 25, 220 (c) 25, 15 (d) 115, 105
15. Consider the following class definitions in a hypothetical Object Oriented language that supports inheritance and uses dynamic binding. The language should not be assumed to be either Java or C++, though the syntax is similar. Class P { Class Q subclass of P { void f (int i) { void f (int i) { print (i); print (2*i); } } } } Now consider the following program fragment: P x = new Q ( ); Q y = new Q ( ); P z = new Q ( ); x.f (1); ((P) y).f(1); z.f(1); Here ( (P) y) denotes a typecast of y to P. The output produced by executing the above program fragment will be
------------- For more papers visit: http://onestopgate.com/gate-preparation/ - http://onestopgate.com/gate-preparation/ |