CSE GATE sample paper
Printed From: One Stop GATE
Category: GATE Previous Years Test Papers - Discuss Here
Forum Name: CS Papers
Forum Discription: Computer Science Previous Year GATE Papers to can discussed here.
URL: http://forum.onestopgate.com/forum_posts.asp?TID=80
Printed Date: 19Sep2025 at 2:24am
Topic: CSE GATE sample paper
Posted By: Priya
Subject: CSE GATE sample paper
Date Posted: 05Jan2007 at 5:45pm
|
1. Which of the following suffices to convert an arbitrary CFG to an LL(1) grammar ? (a) Removing left recursion alone (b) Factoring the grammar alone (c) Removing left recursion and factoring the grammar (d) None of the above
2. Assume that the SLR parser for a grammar G has n 1 states and the LALR parser for G has n 2 states. The relationship between n l and n 2 is (a) n 1 is necessarily less than n2 (b) n 1 is necessarily equal to n2 (c) n 1 is necessarily greater than n2 (d) none of the above
3. In a bottom-up evaluation of a syntax directed definition, inherited attributes can (a) always be evaluated (b) be evaluated only if the definition is L-attributed (c) be evaluated only if the definition has synthesized attributes (d) never be evaluated
4. Suppose the numbers 7, 5, 1, 8, 3, 6, 0, 9, 4, 2 are inserted in that order into an initially empty binary search tree. The binary search tree uses the usual ordering on natural numbers. What is the in-order traversal sequence of the resultant tree?
5. Consider the following three claims
Which of these claims are correct? (a) I and II (b) I and III (c) II and III (d) I, II and III
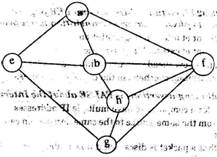
6. Consider the following graph
Among the following sequences
Which are depth first traversals of the above graph? (a) I, II and IV only (b) I and IV only (e) II, III and IV only (d) I, III and IV only 7. The usual Q (n2) implementation of Insertion Sort to sort an array uses linear search to identify the position where an element is to be inserted into the already sorted part of the array. If, instead, we use binary search to identify the position, the worst case running time will (a) remain Q (n 2) (b) become Q (n (log n) 2) (e) become Q (n log n) (d) become Q (n)
8. In a heap with n elements with the smallest element at the root, the 7 th smallest element can be found in time
9. Which of the following statements is FALSE? (a) In statically typed language, each variable in a program has a fixed type (b) In un-typed languages, values do not have any types (c) In dynamically typed languages, variables have no types (d) In all statically typed languages, each variable in a program is associated with values of only a single type during the execution of the program
10. Using a larger block size in a fixed block size file system leads to
11. In a system with 32 bit virtual addresses and 1 KB page size, use of one-level page tables for virtual to physical address translation is not practical because of (a) the large amount of internal fragmentation (b) the large amount of external fragmentation (c) the large memory overhead in maintaining page tables (d) the large computation overhead in the translation process
12. Which of the following assertions is FALSE about the Internet Protocol (IP)? (a) It is possible for a computer to have multiple IP addresses (b) IP packets from the same source to the same destination can take different routes in the network (c) IP ensures that a packet is discarded if it is unable to reach its destination within a given number of hops (d) The packet source cannot set the route of an outgoing packets; the route is determined only by the routing tables in the routers on the way
13. Which of the following functionalities must be implemented by a transport protocol over and above the network protocol? (a) Recovery from packet losses (b) Detection of duplicate packets (c) Packet delivery in the correct order (d) End to end connectivity
14. Which of the following scenarios may lead to an irrecoverable error in a database system?
15. Consider the following SQL query select distinct a 1. a 2, ...... , a n from r 1, r 2……….., r m where P
For an arbitrary predicate P, this query is equivalent to which of the following relational algebra expressions? (a) (b) (c) (d) ------------- For More Sample Papers Visit: http://onestopgate.com/gate-preparation/ - http://onestopgate.com/gate-preparation/ |