GATE latest (CS) question paper
Printed From: One Stop GATE
Category: GATE Previous Years Test Papers - Discuss Here
Forum Name: CS Papers
Forum Discription: Computer Science Previous Year GATE Papers to can discussed here.
URL: http://forum.onestopgate.com/forum_posts.asp?TID=7
Printed Date: 19Sep2025 at 1:45am
Topic: GATE latest (CS) question paper
Posted By: Salini
Subject: GATE latest (CS) question paper
Date Posted: 27Dec2006 at 3:56pm
|
1 X, Y and Z are closed intervals of unit length on the real line. The overlap of X and Y is half a unit. The overlap of Y and Z is also half a, unit. Let the overlap of X and Z be k units. Which of the following is true?
The value of Pr (E 1), the probability of the event E p is
3 Let and Which of the following statements is true?
4 A polynomial p(x) satisfies the following: p (1) = p(3) = p(5) = 1 p(2) = p(4) = -1 The minimum degree of such a polynomial is
5 A relation R is defined on the set of integers as x Ry if f(x + y) is even. Which of the following statements is true?
6 Let P(S) denotes the power set of set S. Which of the following is always true?
7 Let a, b, c, d be propositions. Assume that the equivalences a « (b V-b) and b « c hold. Then the truth value of the formula (a Ù b) -J. (a Ù c) Ù d) is always
8 What can be said about a regular language L over {a} whose minimal finite state automaton has two states?
9 Consider the following decision problems : (PI) Does a given finite state machine accept a given string (P2) Does a given context free grammar generate an infinite number of stings Which of the following statements is true? (a) Both (PI) and (P2) are decidable (b) Neither (PI) nor (P2) are decidable (c) Only (PI) is decidable (d) Only (P2) is decidable
10 The simultaneous equations on the Boolean variables x, y, z and w, x+y+z=l xy =0 xz+w = l x+ have the following solution for x, y, z and w, respectively. (a) 0 1 0 0 (b) 1 1 0 1 (c) 1 0 1 1 (d) 1 0 0 0
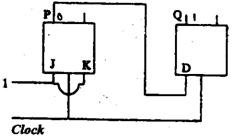
11 Which function does NOT implement the Karnaugh map given below?
(a) (w + x) y (b) xy + yw (c) (w + x) (w + y) (x + y) (d) None of the above
13 A graphics card has on board memory of 1 MB. Which of the following modes can the card not support? (a) 1600 x 400 resolution with 256 colours on a 17-inch monitor (b) 1600 x 400 resolution with 16 million colours on a 14-inch monitor (c) 800 x 400 resolution with 16 million colours on a 17-inch monitor (d) 800 x 800 resolution with 256 colours on a 14-inch monitor
14 Consider the values A = 2.0 x 10 30, B =-2.0 x 10 30 , C= 1.0, and the sequence X: =A+B Y: =A+C X: = X + C Y: =Y+B executed on a computer where floating-point numbers are represented with 32 bits. The values for X and Y will be
15 Suppose you are given an array s[1..n] and a procedure reverse (s, i, j) which reverses the order of elements in a between positions i and j (both inclusive). What does the following sequence do, where 1 £ k £ n: reverse (s, 1, k) ; reverse (s, k + 1, n); reverse (s, l, n) ; (a) Rotates s left by k positions (b) Leaves s unchanged (c) Reverses all elements of s (d) None of the above
16 Let LASTPOST, LASTIN and LASTPRE denote the last vertex visited in a postorder, inorder and preorder traversal, respectively, of a complete binary tree. Which of the following is always true? (a) LASTIN = LASTPOST (b) LASTIN = LASTPRE (c) LASTPRE = LASTPOST (d) None of the above
17 Consider the following functions
Which of the following is true? (a) h (n) is O (f (n) ) (b) h (n) is O (g (n)) (c) g (n) is not O (f (n) ) (d) f(n) is O(g (n)) |
 1,0
1,0