GATE-1999 Instrumentation Engg
Printed From: One Stop GATE
Category: GATE Previous Years Test Papers - Discuss Here
Forum Name: ECE Papers
Forum Discription: ECE Previous Year GATE Papers to can discussed here.
URL: http://forum.onestopgate.com/forum_posts.asp?TID=85
Printed Date: 08Feb2025 at 10:20pm
Topic: GATE-1999 Instrumentation Engg
Posted By: Neha Agarwal
Subject: GATE-1999 Instrumentation Engg
Date Posted: 05Jan2007 at 6:08pm
|
1.1. (a) 0 (b) 1.1 (c) 0.5 (d) 1
1.2. For the waveform V (t) = 2 + cos (a) (c) p (d) 1.3. A system with transfer function (a) 6.9 s (b) 10 s (c) 14.4 s (d) 20 s
The transfer function of this system is (a) (b) (c) 1+ s 2e -2s
(d) 1+ s 2e 2s
1.5. A transfer function has two zeroes at infinity. Then the relation between the numerator degree (N) and the denominator degree (M) of the transfer function is, (a) N=M+2 (b) N=M-2 (c) N=M+1 (d) N=M-l
(a) 0.8 (c) -0.4 (b) 0.4 (d) unbounded
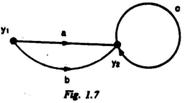
1.7. The transfer function betweenY 2 and Y 1 in Fig. 1.7 is
(a) a+b (b) (a+b)c (C) (d)
1.8. In control system design, gain and phase margins are usually provided to (a) account for the uncertainties in the system (b) make the system respond fast (c) reduce the overshoot in step response (d) reduce the steady state offset. 1.9. The lengths of two discrete time sequences X 1 (n) are 5 and 7 respectively. The maximum length of sequence x 1 (n) * x 2(n) is (a) 5 (b) 6 (c) 7 (d) 11
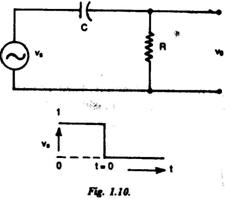
1.10. The output voltage of the circuit in Fig. 1.10 for t > 0 is
(b) (c) (d)
1.12. The input voltage, V 1 is 4 + 3 sin wt. assuming all elements to be ideal, the average of the output voltage V o in Fig. 1.12 is (a) -3 V (b) +3 V (c) -7 V (d) +7 V
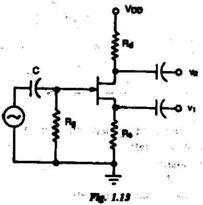
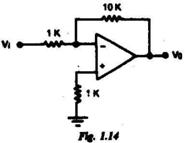
1.13. In the JFET amplifier circuit shown in Fig. 1.13, the signal outputs V 1 and v 2 are related as (a) (b) (c) (d) 1.14. The op-amp in the amplifier circuit shown in Fig. 1.14 has an offset voltage of 10 mV and it is ideal otherwise. If V i is zero, the output voltage V o is
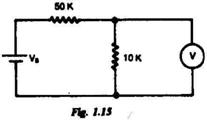
1.15. A voltmeter connected across the 10 k W resistor in the Fig. 1.15, reads 5 V. The voltmeter is rated at 1000 ohms/volt and has a full scale reading of 10 V. The supply voltage V s in volt is
------------- For more papers visit: http://onestopgate.com/gate-preparation// - http://onestopgate.com/gate-preparation// |
 (a)
(a) 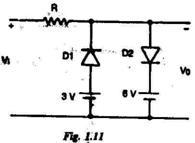 3V
3V 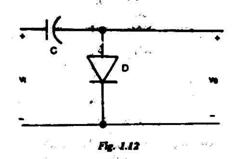
 0
0