CSE GATE sample paper
Printed From: One Stop GATE
Category: GATE Previous Years Test Papers - Discuss Here
Forum Name: CS Papers
Forum Discription: Computer Science Previous Year GATE Papers to can discussed here.
URL: http://forum.onestopgate.com/forum_posts.asp?TID=69
Printed Date: 18Sep2025 at 2:40am
Topic: CSE GATE sample paper
Posted By: Neha Agarwal
Subject: CSE GATE sample paper
Date Posted: 05Jan2007 at 5:04pm
|
1.If one uses straight two-way, merge sort algorithm to sort the following elements in ascending order: 20, 47, 15, 8, 9, 4, 40, 30, 12, 17 then the order of these elements after second pass of the algorithm is :
2. If n is a power of 2, then the minimum number of multiplications needed to compute a* is
3. Which of the following is the most powerful parsing method?
4. Consider the join of a relation R with a relation S. If R has m tuples and S has n tuples then the maximum and minimum sizes of the join respectively are
5. The relational algebra expression equivalent to the following tuple calculus expression: {t | t Î r Ù (t [A] = 10 Ù t = 20)} is :
6. Booth's coding in 8 bits for the decimal number - 57 is
7. The maximum gate delay for any output to appear in an array multiplier for multiplying two n bit number is
8. The main memory of a computer has 2 cm blocks while the cache has 2 c blocks. If the cache uses the set associative mapping scheme with 2 blocks per set, then block k of the main memory maps to the set
9. The Newton-Raphson method is to be used to find the root of the equation f (x) = 0 where Xo is the initial approximation and f 1 is the derivative of f. The method converges
10. Let R = (a, b, c, d, e, f) be a relation scheme with the following dependencies c ® f, e ® a, ec ® d, a ® b. Which of the following is a key for R ?
11. Which of the following is correct?
------------- For more papers visit: http://onestopgate.com/gate-preparation// - http://onestopgate.com/gate-preparation// |
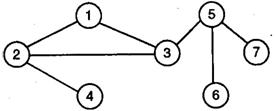 The number of articulation points of the following graph is
The number of articulation points of the following graph is